Temporomandibular joint dislocation
What is temporomandibular joint dislocation?
Temporomandibular joint dislocation refers to the condyle (mandibular joint head or mandibular head) slipping out of the joint socket, exceeding the normal range of joint movement, making it unable to return to its original position on its own.
The most common type is acute anterior dislocation of the temporomandibular joint. Unilateral dislocation is common, but bilateral dislocation can also occur simultaneously.
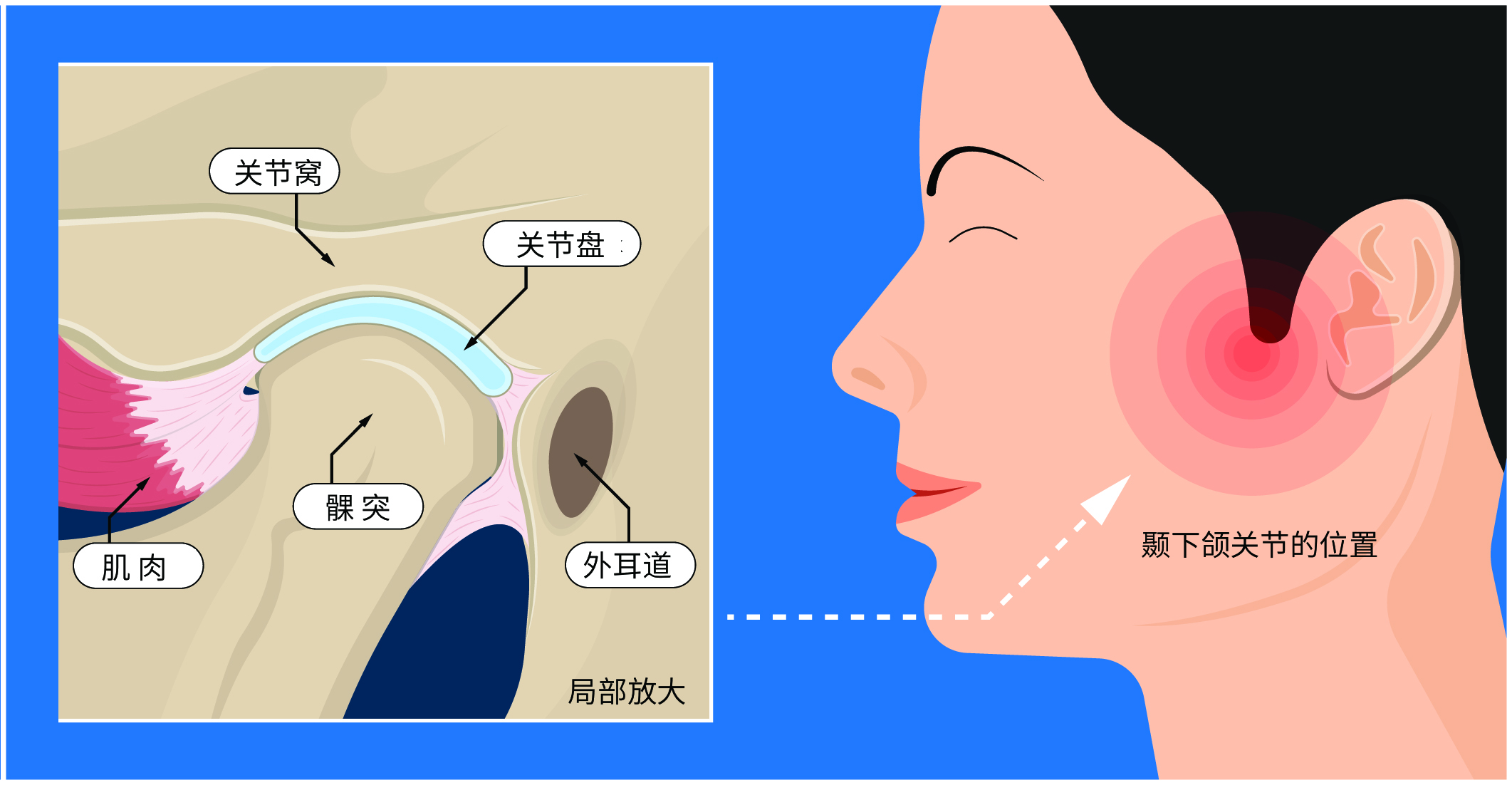
What causes temporomandibular joint dislocation?
- Excessive mouth opening: Actions like yawning, laughing, or biting large pieces of food can cause dislocation due to excessive mouth opening.
- Temporomandibular joint disorder: Patients with this condition may experience dislocation during normal activities like speaking or eating.
- External force impact: Violent external impact on the joint or jaw can also lead to dislocation.
Who is most susceptible to temporomandibular joint dislocation?
It is common among middle-aged and elderly individuals and those with temporomandibular joint disorders, but it can also occur in adolescents.
What are the main symptoms of temporomandibular joint dislocation?
- Malocclusion: The mouth remains partially open, and teeth cannot close properly.
- Facial appearance: The chin protrudes forward or deviates (toward the dislocated side), making it impossible to close the mouth. A thumb-sized depression may be visible in front of the tragus.
- Other symptoms: Inability to close the mouth may lead to drooling, slurred speech, and difficulty swallowing.
Which department should be consulted for temporomandibular joint dislocation?
Generally, patients should visit the dentistry department. If subspecialties are available, oral and maxillofacial surgery is recommended.
How is temporomandibular joint dislocation diagnosed?
Characteristic symptoms like an open mouth, inability to bite, and drooling are usually sufficient for diagnosis.
X-rays, dental CT scans, or spiral CT scans can confirm the dislocation. In cases of severe external impact, these imaging tests can also determine if there is a condylar fracture and its location.
How is temporomandibular joint dislocation treated?
Manual reduction: Most patients can undergo manual reduction of the temporomandibular joint. After reduction, a bandage is typically used to immobilize the jaw for 2 weeks.
Sclerosing agent therapy: For habitual dislocation patients, sclerosing agent injections may be used.
Surgical treatment: For some patients with habitual or chronic dislocations unresponsive to sclerosing agent therapy, surgery may be necessary.
What is the prognosis for temporomandibular joint dislocation?
The overall prognosis for temporomandibular joint dislocation is good.
- Prompt reduction after dislocation has minimal impact on daily life.
- Patients with habitual dislocation may fear recurrence, avoiding wide mouth opening while eating or speaking, or subconsciously supporting their chin during these activities.
How can temporomandibular joint dislocation be prevented?
- At the first occurrence of dislocation, seek medical help immediately. Self-attempts at manual reduction are not advised to avoid further damage to the joint or ligaments.
- Avoid excessive mouth opening when yawning or eating, and refrain from consuming large pieces of food.
- Maintain adequate rest, avoid staying up late, and prevent excessive fatigue.
- During physical activities, protect the jaw to avoid strong external impacts.
- Maintain a positive and healthy mental state.