papule
SYMPTOMS
What Diseases Do Papules Generally Indicate?
Papules are not a disease but refer to flat, round, umbilicated, or nipple-like rashes raised above the skin surface, typically less than 1 cm in diameter. Their color may match the skin tone or appear red (drug rash, measles, etc.), yellow (xanthoma), white (milia), black (pigmented nevus), or purple (lichen planus)[1,2]. Depending on the cause, papules may appear in different areas with varying symptoms. Common clinical manifestations include:
- Common Warts: Caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), they are a frequent skin condition, colloquially called "warts," and can occur anywhere on the body, often on the hands. Initially appearing as pinhead-sized papules, they gradually enlarge to pea-sized or larger, grayish-brown, brown, or skin-colored, rough-surfaced, and firm to the touch[3]. Most are asymptomatic, though some may be tender.
- Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus: Often appears on the upper trunk, face, neck, and other sun-exposed areas. The cause is unclear, but environmental factors (UV exposure), certain medications (e.g., procainamide, isoniazid, penicillin), and infections (e.g., streptococcus, EBV) may trigger or worsen it. Early symptoms include small papules that expand. The condition is UV-sensitive, typically heals without scarring but may cause pigment changes or telangiectasia[4].
- Rosacea (Papulopustular Type): Commonly affects the face. Potential triggers include genetics, immune dysfunction, environmental factors (temperature changes, sun exposure, cooking fumes), and improper skincare. Red, dome-shaped papules and superficial pustules may develop on erythematous patches. Usually painless and non-scarring, but some patients report stinging, itching, or dryness[5].
- Milia: Known as "fat granules," these often appear around the eyes. Primary milia have no clear cause, while secondary milia may follow trauma, frostbite, or skin diseases. They manifest as 1–3 mm white or pale yellow, dome-shaped papules, solitary or clustered. Most resolve spontaneously; persistent cases may require medical treatment[4].
- Lichen Planus: Typically occurs on flexural surfaces (e.g., inner wrists, elbows). Characterized by violaceous, polygonal, flat-topped papules. Oral involvement is possible, often with intense itching[4].
- Erythema Multiforme: The erythema-papule type commonly affects the face, neck, and extensor surfaces (e.g., back of hands, thighs). Triggers include infections, drugs, food, trauma, or radiation. Lesions are primarily erythematous, possibly with itching, mild pain, or burning[4].
What Might Papules Look Like?
Papules are not a disease but a manifestation of various skin conditions. They are typically flat, round, umbilicated, or nipple-like, raised lesions under 1 cm in diameter. Colors range from skin-toned to red (drug rash, measles), yellow (xanthoma), white (milia), black (pigmented nevus), or purple (lichen planus). Appearance varies by cause and location:
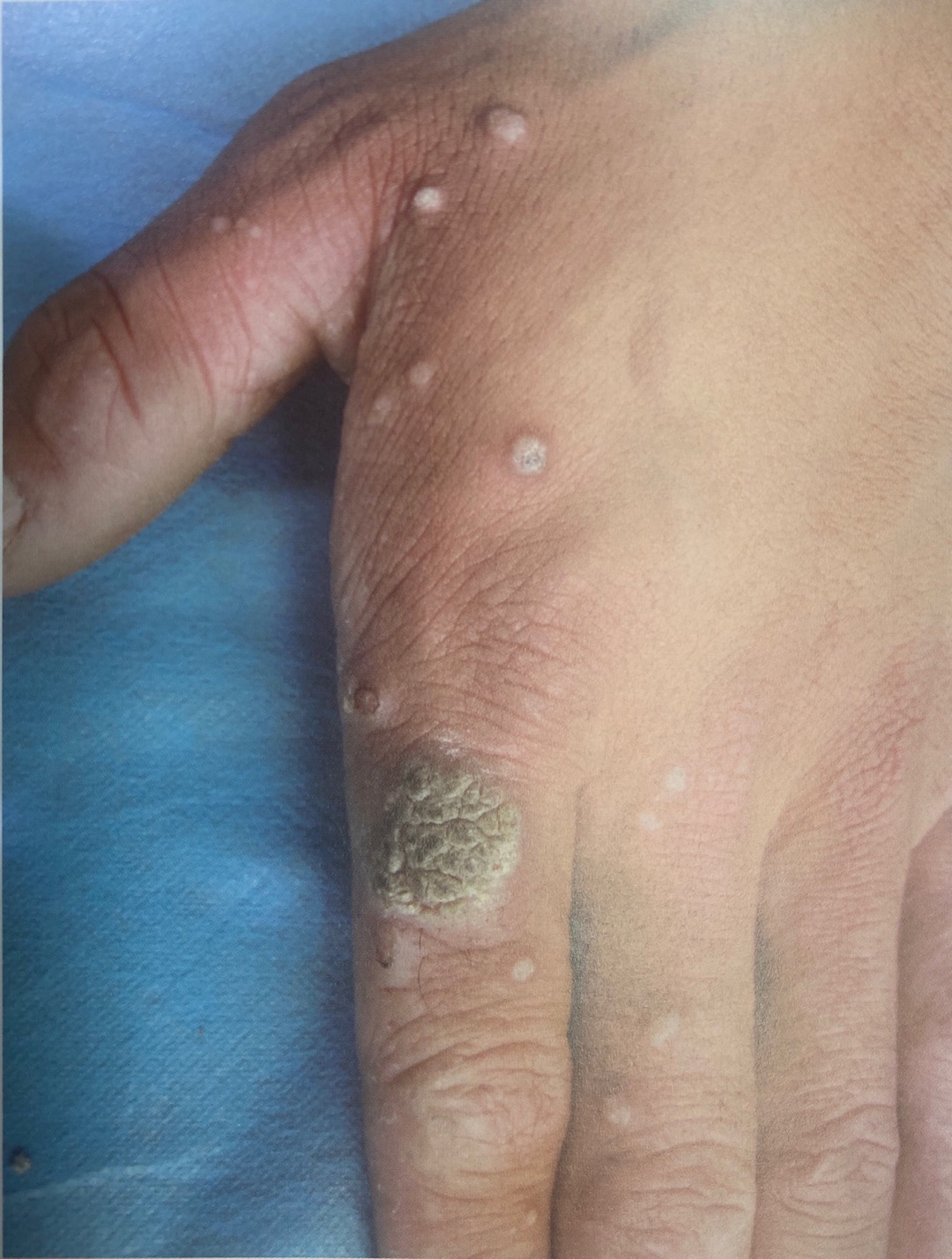
Rough surface, cauliflower-like or spiky texture, firmer than surrounding skin.
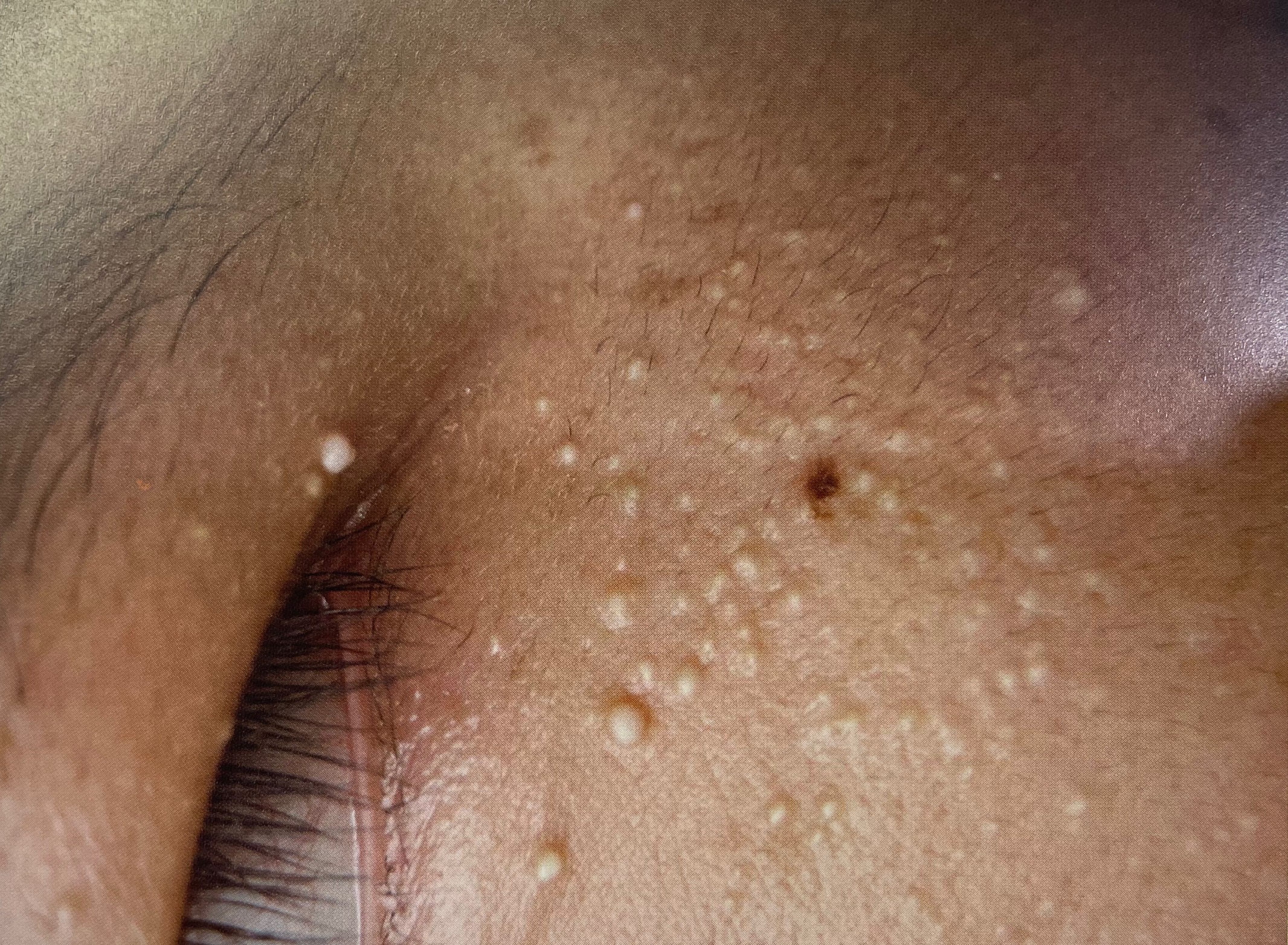
Yellowish-white small papules on eyelids/cheeks, smooth and firm.
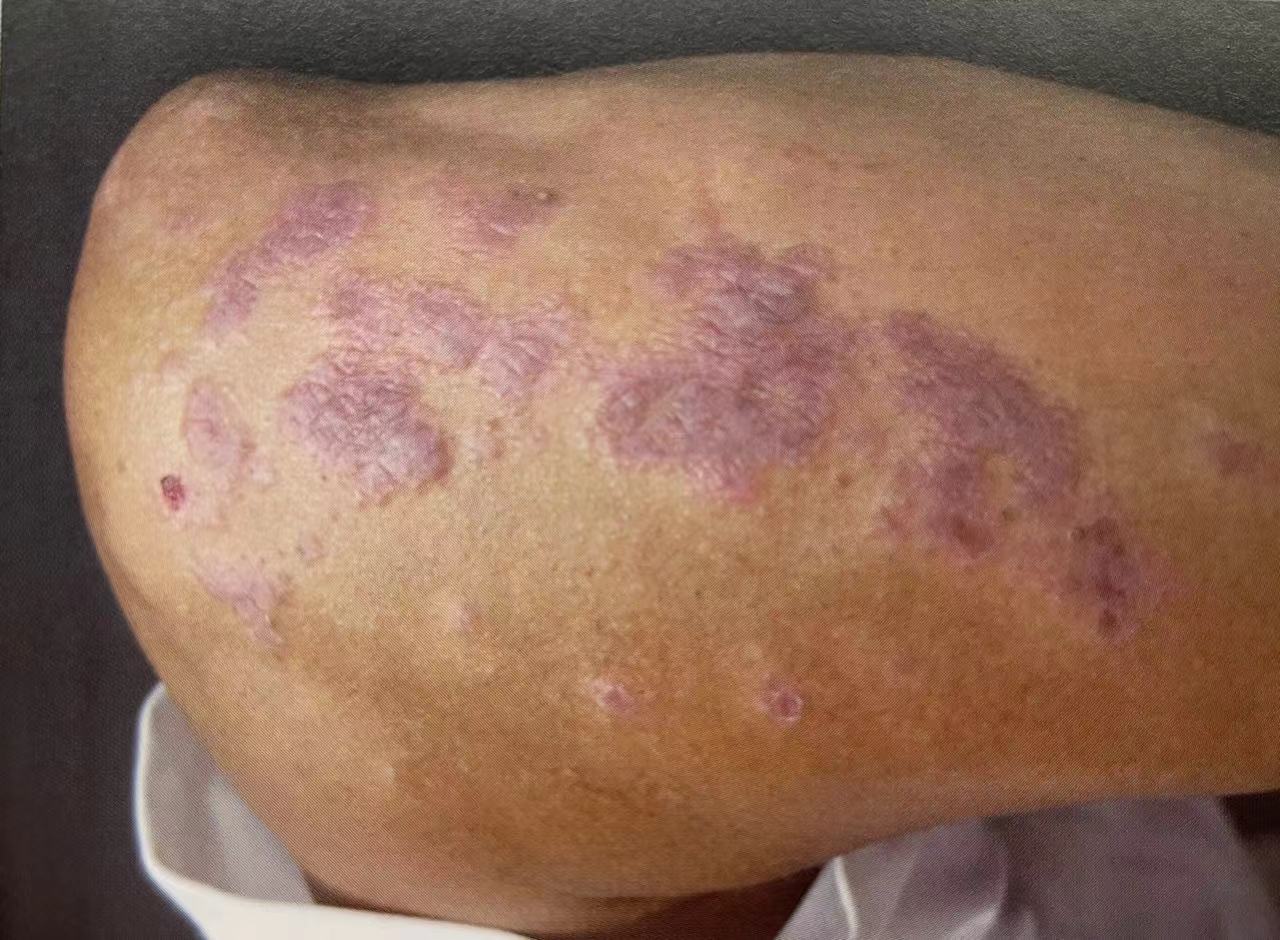
Violaceous flat papules/plaques on elbows, glossy surface.
Image source: Atlas of Dermatological Diagnosis
TREATMENT
Can Papules Be Cured?
Generally, they can be cured. For example, common warts may resolve on their own, with a 90% natural clearance rate within 5 years[4]. Some papules, such as milia and erythema multiforme with erythematous papules, can also disappear spontaneously. Others, like subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus and rosacea, can achieve good results with systematic and appropriate treatment.
How to Treat Papules?
Most papules are treated with medications, surgery, or other methods. Common approaches include:
-
General Treatment: For papules caused by external factors, avoiding the triggers can help. For example, drug-induced milia may resolve after discontinuing the medication[4]. If papules result from chronic diseases, treating the underlying condition can lead to their improvement or disappearance.
-
Medication:
-
For viral-induced papules (e.g., common warts, molluscum contagiosum), antiviral drugs like interferon may be prescribed for extensive cases.
-
For fungal infections (e.g., tinea corporis), antifungal medications such as ketoconazole can be used as directed.
-
Corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone, hydrocortisone, dexamethasone) may be prescribed for conditions like lichen planus or lupus-related papules. Due to potential side effects, especially with systemic use, these should be taken under medical supervision.
- Dermatologic Surgery: Molluscum contagiosum can be treated with curettage (disinfecting the skin, then using forceps to extract the lesion). Changing or atypically located pigmented moles may require surgical excision.
- Physical Therapy: Cryotherapy, electrocautery, or laser treatment can address papules like warts, flat warts, or milia[4].
Dietary Considerations for Papule Patients
- Maintain a balanced diet with fresh fruits, vegetables, and light meals.
- Avoid high-fat foods (e.g., fried chicken, fatty pork) to prevent excess oil from worsening skin conditions.
Lifestyle Tips for Papule Patients
- Clean skin regularly, practice proper skincare, change clothes daily, and replace bedding frequently. Opt for cotton fabrics.
- After procedures like needle extraction or physical therapy, keep the wound dry and clean. Let scabs fall off naturally—avoid scratching to prevent infection.
- Get adequate rest, avoid excessive fatigue or late nights, and engage in moderate exercise (e.g., jogging) to boost immunity.
- Avoid exposing affected skin to harsh chemicals like alkaline soaps or cleansers.
Self-Monitoring for Papule Patients
Monitor changes in papule count, size, color, or shape. Seek medical attention if redness, swelling, or breaks occur around the lesions.
Family Support for Papule Patients
Since papules may cause appearance-related anxiety, family members should pay attention to the patient’s mental health. Encourage open communication to prevent emotional distress, and seek professional psychological help if needed.
DIAGNOSIS
Under what circumstances should patients with papules seek medical attention?
- When small red or skin-colored bumps appear on the skin, further examination under a doctor's guidance is necessary.
- Seek prompt medical attention if papules spread extensively.
- Immediate medical care is required if redness, swelling, or breakage occurs around the lesions.
- Seek timely medical help if the color or shape of the papules changes significantly.
Which department should patients with papules visit first?
Dermatology.
What examinations are required for papules during a medical visit?
Most diseases causing papules require comprehensive diagnosis based on physical examination (with emphasis on skin lesion examination), fungal microscopy, and other tests.
- Physical examination: A thorough examination under adequate lighting and warm conditions to observe the size, shape, and distribution of lesions. Magnifying glasses or dermatoscopes may be used if necessary[4].
- Visual inspection: Small raised papules may be visible on the skin surface[2].
- Fungal microscopy: Results vary depending on the papular disease. For suspected fungal infections, microscopic examination of scraped skin scales can identify pathogens, aiding diagnosis and differentiation from other conditions[2].
POTENTIAL DISEASES
What Causes Papules?
- Infectious factors: Bacteria, viruses, fungi, etc., invading the body may cause infections, such as cutaneous tuberculosis, common warts, etc.
- Physical factors: Physical factors like sun exposure or friction may lead to papules, such as frictional lichenoid eruptions.
- Disease factors: Papules caused by other conditions, such as autoimmune disorders (e.g., lupus erythematosus), endocrine or metabolic issues (e.g., porphyria), or hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., contact dermatitis, papular urticaria)[4].
What Diseases May Be Associated with Papules?
Papules may be related to conditions like drug eruptions, measles, and eczema[2].
Are Papules Hereditary?
Some diseases causing papules may have genetic links. For example, the cause of lichen planus remains unclear but may involve heredity[4].
Lupus erythematosus also shows familial clustering, with a heritability of 43%[4].
Rosacea may also develop as a skin condition influenced by genetic background[4].
