Angina
OVERVIEW
What part of the body is the isthmus of fauces?
The isthmus of fauces is a narrow ring-shaped structure in the oropharynx, formed by the uvula, the posterior edge of the soft palate, the left and right palatoglossal arches, and the base of the tongue. It serves as the opening connecting the oral cavity and the pharynx.
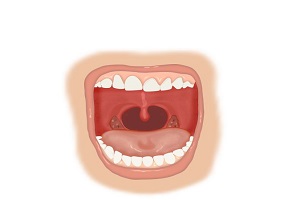
What is angina?
Inflammation occurring in the isthmus of fauces is collectively referred to as angina. The inflammation can be caused by various pathogens such as viruses and bacteria, with symptoms mainly including sore throat, fever, difficulty swallowing, etc. In infants, it primarily manifests as fever, refusal to eat, and irritability.
Depending on the pathogen, angina can be further classified into several types, the most common of which is "herpangina," a term familiar to many parents.
Angina caused by viruses usually has no specific medication and can be managed with fever-reducing and pain-relieving treatments to alleviate discomfort while waiting for the body to recover naturally. For angina caused by bacteria or other pathogens, appropriate antimicrobial medications may be used.
Most cases of angina are not severe and resolve within 1–2 weeks. Angina is contagious, so avoiding contact with infected individuals, frequent handwashing, boosting immunity, and maintaining oral hygiene can help reduce the risk of developing angina.
What are the special types of angina?
-
Herpangina: The most common type, caused by enteroviruses such as Coxsackievirus A and Epstein-Barr virus. Symptoms include sudden fever, sore throat, dry throat, foreign body sensation, herpes, ulcers, etc., often accompanied by upper respiratory tract infections. Most cases are mild and resolve on their own within 1–2 weeks, though some may progress to hand, foot, and mouth disease.
-
Ludwig's angina: Also known as submandibular space infection, it is relatively rare and caused by bacteria, resulting in widespread acute cellulitis in the submandibular, sublingual, and submental regions. Symptoms include sudden onset with chills, high fever, sore throat, and in some cases, difficulty breathing due to airway obstruction. This condition is severe and progresses rapidly, potentially becoming life-threatening if not treated properly.
-
Vincent's angina: Also called trench mouth or acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis, it is now very rare and primarily caused by infection with Fusobacterium and Vincent's spirochete. These pathogens can exist in the mouths of healthy individuals at low virulence without causing disease. However, when immunity weakens, they rapidly multiply, increase in virulence, and lead to infection.
SYMPTOMS
What are the symptoms and manifestations of angina?
Different types of angina present differently.
What are the symptoms and manifestations of herpangina, a common type of angina?
Herpangina is more prevalent in summer and autumn, mostly affecting children aged 3–10. The main manifestations include:
-
Fever: Sudden high fever, with temperatures reaching 39–41°C, often accompanied by lethargy and limb pain. Some children may experience febrile seizures.
-
Sore throat: The pain often affects eating, and infants may vomit or refuse food.
-
Oral blisters and ulcers: Small gray papules may appear in the throat, developing into blisters and ulcers within 24 hours, surrounded by a 1–5 mm red halo. A few cases may develop bacterial infections, leading to pustules.
-
Other accompanying symptoms: Herpangina may be accompanied by bad breath, gum bleeding, and swollen submandibular lymph nodes.
Fever typically subsides in 3–5 days, ulcers heal, throat pain lessens, and eating improves. Most children recover within 1–2 weeks.
What are the symptoms and manifestations of Ludwig's angina?
-
Initial symptoms include fever, toothache, and sore throat.
-
The infection can spread rapidly, causing restricted mouth opening, difficulty swallowing, and breathing problems.
-
If symptoms worsen, life-threatening complications may occur, such as airway obstruction, neck vessel rupture, mediastinitis, sepsis, pericarditis, toxic shock, or multi-organ failure.
What are the symptoms and manifestations of Vincent's angina?
Vincent's angina is common in adolescents or infants.
Main symptoms include gum pain, worsened by eating, speaking, or swallowing, along with headache, muscle pain, malaise, and fever. A foul odor is noticeable, and submandibular lymph nodes may swell.
Complications are rare, but pathogens may spread to nearby areas (eyes, ears, sinuses, throat, lungs) or distant sites (intestines, appendix, brain), or cause bacteremia.
CAUSES
What are the causes of angina?
Angina can be caused by various viruses, bacteria, and spirochetes. For example:
-
Herpangina: Caused by enteroviruses such as Coxsackievirus A and Epstein-Barr virus.
-
Ludwig's angina: Often caused by mixed infections of hemolytic streptococcus and anaerobic bacteria.
-
Vincent's angina: Caused by infections of Fusobacterium and Vincent's spirochete.
Is angina contagious?
Yes.
It is generally transmitted through close contact between people. In children, transmission is often related to contact with toys, hands, utensils, towels, etc., and may also occur through droplets.
Therefore, it is important to wash hands frequently, keep living spaces ventilated, and wear masks when in crowded or enclosed places.
Who is commonly affected by angina?
Different types of angina are common in different populations. For example:
-
Herpangina: Mostly seen in children aged 3–10, who may experience multiple episodes within a year. It often occurs secondary to acute rhinitis, pneumonia, influenza, malaria, or epidemic meningitis, but can also occur independently.
-
Bacterial angina: More likely to occur in people with oral diseases such as periodontal abscess, periapical periodontitis, or pericoronitis. Those who frequently stay up late, have irregular routines, drink little water, consume excessive spicy or greasy foods, or neglect oral hygiene are also more susceptible.
-
Vincent's angina: Often occurs in individuals with weakened immunity, poor oral hygiene, malnutrition, poor environmental conditions, vitamin deficiencies, or chronic illnesses. Smokers are more prone to it than non-smokers.
DIAGNOSIS
How is angina diagnosed?
Doctors can generally diagnose angina by reviewing medical history, assessing symptoms, and examining the oropharynx. Identification of the pathogen through smear tests, cultures, or other examinations can confirm the diagnosis. For example:
-
Herpangina: Culturing throat vesicle fluid or stool to isolate Coxsackievirus or Echovirus confirms the diagnosis. Special neutralizing antibody-complement fixation or hemagglutination inhibition tests during the acute and recovery phases also aid in diagnosis.
-
Ludwig's angina: Pus culture identifying pathogenic bacteria confirms the diagnosis.
-
Vincent's angina: Throat swab cultures detecting Fusobacterium and Spirochetes provide confirmation. Physical examination revealing a gray-white or yellow-white, irregular-edged, deep burrowing ulcer with pseudomembrane on one tonsil upper pole, along with smear tests identifying Fusobacterium and Spirochetes, also confirms the diagnosis.
TREATMENT
Which department should patients with angina go to for treatment?
Generally, patients with mild angina can visit the ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) department or pediatric ENT (Pediatrics) clinic.
Those with severe fever should go to the fever clinic. If severe angina causes airway obstruction or unstable vital signs, immediate emergency department treatment is required.
What are the treatment methods for angina?
Treatment plans vary depending on the type of angina. Here are some common treatment methods:
-
Anti-infection therapy: There are no specific antiviral drugs for viral angina, and the body needs to recover naturally. Bacterial or spirochete-induced angina can be treated with appropriate antibiotics. Before test results are available, empirical antibiotics may be used, and targeted antibiotics should be administered as soon as sensitivity results are obtained.
-
Symptomatic and supportive therapy: Includes rest, isolation, increased fluid intake, improved nutrition, fever reduction, and pain relief to alleviate discomfort and promote recovery.
-
Oral care: Regular oral hygiene and the use of mouthwash to help control infection.
-
Other: Ludwig's angina is usually severe and may require special treatments such as maintaining airway patency and abscess incision and drainage.
You can search for specific types of angina to learn more details.
Is angina serious?
-
Herpangina: Most cases are not severe and resolve on their own.
-
Ludwig's angina: Can become very severe, leading to life-threatening complications such as airway obstruction, septic shock, sepsis, or even acute mediastinal infection.
-
Vincent's angina: Often occurs in individuals with weakened immunity, tends to recur, and is difficult to treat.
DIET & LIFESTYLE
What should patients with angina pay attention to in their diet?
-
Since angina can cause significant pain, it may affect normal eating. When the pain is severe, opt for light, easily digestible liquid or semi-liquid foods to reduce discomfort during meals, such as porridge, milk, soy milk, noodles, or wontons. Resume a more nutritious diet as soon as the pain subsides. Avoid eating nothing due to pain, as this is not conducive to recovery.
-
Drink plenty of water. Fever can lead to significant fluid loss, and reduced eating due to pain may also result in insufficient fluid intake, so it's important to stay hydrated. If unable to eat or drink at all, seek medical attention to assess for dehydration and receive intravenous fluids if necessary.
-
Avoid spicy and irritating foods.
-
Eating cold foods like ice cream or chilled fruit juice may help relieve pain and can be tried.
What should patients with angina pay attention to in daily life?
-
Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol.
-
Rinse your mouth promptly after eating or drinking.
-
Since the condition is contagious during the illness, isolate and disinfect personal items to avoid spreading it to others.
-
Seek medical attention promptly if symptoms worsen.
PREVENTION
How to Prevent Pharyngitis?
Pharyngitis, especially herpangina, is contagious, making prevention particularly important. Preventive measures include:
-
Wash hands frequently with soap or hand sanitizer.
-
Maintain oral hygiene and treat oral diseases promptly.
-
Avoid exposing children and immunocompromised individuals to poorly ventilated public spaces. Ensure proper ventilation at home and regularly air out bedding.
-
Maintain a balanced diet, avoid picky eating, ensure adequate sleep, exercise regularly, and boost immunity.